- 1.1.1 IRS Mission and Organizational Structure
- 1.1.1.1 Purpose of IRM 1.1.1
- 1.1.1.2 IRS Mission
- 1.1.1.3 Statutory Authority
- 1.1.1.4 IRS Values
- 1.1.1.5 Structure of the IRS
- 1.1.1.6 IRS Commissioner
- 1.1.1.6.1 IRS Deputy Commissioner
- 1.1.1.6.1.1 Chief Tax Compliance Officer
- 1.1.1.6.1.2 Chief Operating Officer
- 1.1.1.6.1.3 Chief Taxpayer Services
- 1.1.1.6.1.4 Chief Information Officer
- 1.1.1.6.1.5 Online Services
- 1.1.1.6.2 Organizations Directly Reporting to the IRS Commissioner
- 1.1.1.6.1 IRS Deputy Commissioner
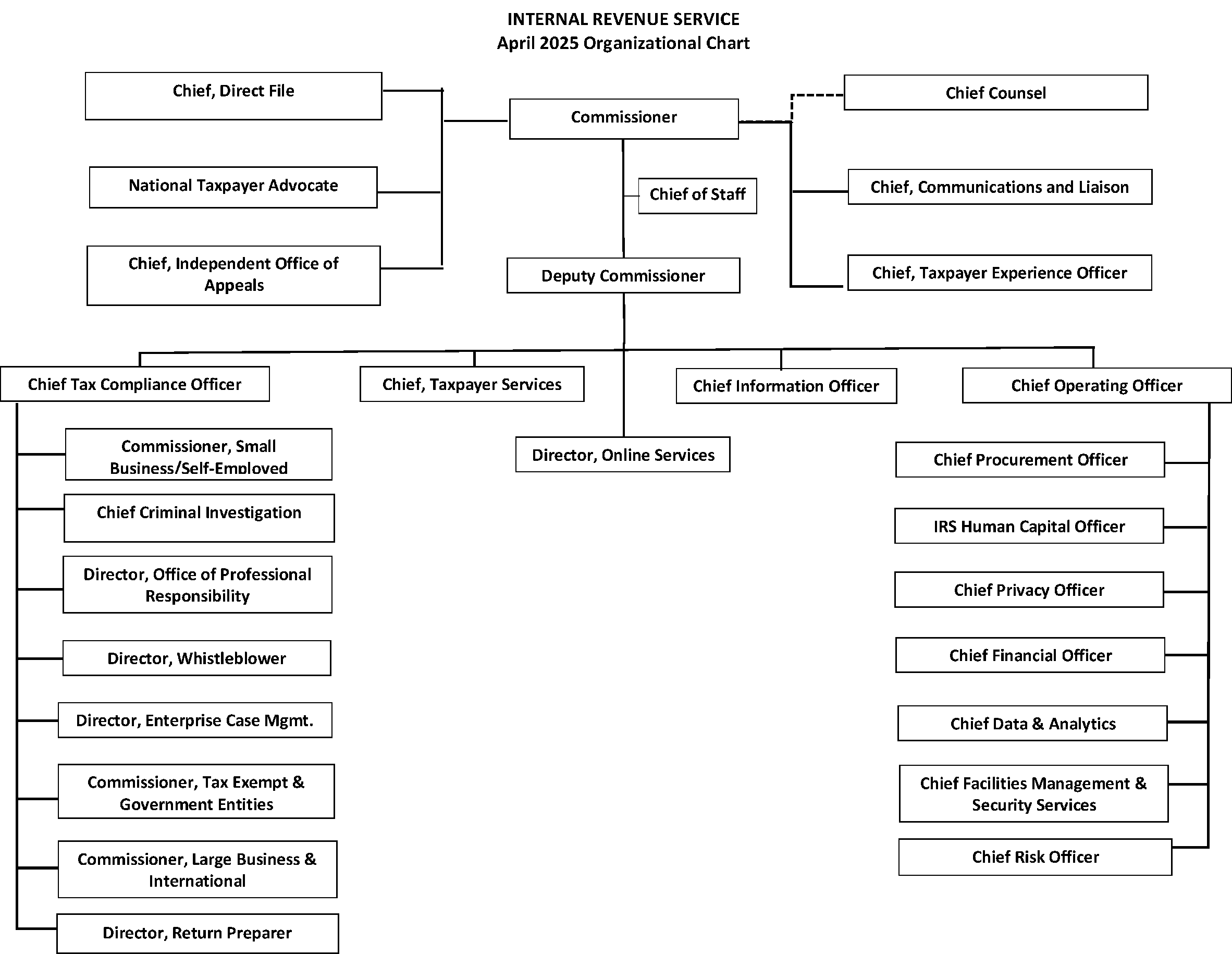
- Exhibit 1.1.1-1 IRS Organization Chart - Internal Revenue Service Organization and Top Officials
Part 1. Organization, Finance, and Management
Chapter 1. Organization and Staffing
Section 1. IRS Mission and Organizational Structure
1.1.1 IRS Mission and Organizational Structure
Manual Transmittal
July 10, 2025
Purpose
(1) This transmits revised IRM 1.1.1, Organization and Staffing, IRS Mission and Organizational Structure.
Material Changes
(1) IRM 1.1.1.1 - Simplified text and language.
(2) IRM 1.1.1.4 - Updated IRS Values to remove statement on inclusion.
(3) IRM 1.1.1.5 - Updated IRS structure based on April 8, 2024, reorganization, current IRS organizational reporting and operations.
-
Updated content to reflect the new structure as of April 8, 2024: IRS Commissioner, single IRS Deputy Commissioner, and four IRS Chiefs (Chief Tax Compliance Officer, Chief Operating Officer, Taxpayer Services, and Chief Information Officer). Removed Deputy Commissioner Services and Enforcement (DCSE) and realigned the organizations under the Chief Compliance Officer and Chief Operating Officer.
-
Removed Equity, Diversity, and Inclusion (EDI) office to reflect new policy.
-
Updated content to reflect the new program offices: Enterprise Case Management Office, Taxpayer Experience Office, and Direct File.
-
Exhibit 1.1.1-1 - Updated to reflect current organizational structure.
(4) Throughout - Content has been updated for plain language, legal references and links, punctuation and editorial corrections. Restructured content in outline numbering format.
Effect on Other Documents
This IRM supersedes IRM 1.1.1 dated July 29, 2019.Audience
All IRS employeesEffective Date
(07-10-2025)Risa W. Kornegay
Deputy Chief of Staff
-
This Internal Revenue Manual (IRM) section explains the mission, statutory authority and organizational structure of the Internal Revenue Service (IRS).
-
The Taxpayer Bill of Rights explains taxpayer rights in plain language and groups them into 10 fundamental rights.
-
The IRS mission:
Provide America's taxpayers top-quality service by helping them understand and meet their tax responsibilities and enforce the law with integrity and fairness to all.
-
This mission statement describes the IRS's role and the public’s expectation about how the IRS should perform that role. Additionally:
-
Congress passes tax laws and requires taxpayers to comply.
-
The taxpayer’s role is to understand and meet their tax obligations.
-
The IRS's role is to help taxpayers understand the tax law, while ensuring that those who do not want to voluntary comply, pay their fair share of tax.
-
-
The IRS is organized to carry out the responsibilities of the Secretary of the Treasury under Internal Revenue Code Section 7801. The Secretary has full authority to administer and enforce the internal revenue laws and the power to create an agency to enforce these laws. The IRS was created based on this legislative grant.
-
Internal Revenue Code Section 7803 provides for the appointment of a Commissioner of Internal Revenue to administer and supervise the execution and application of the internal revenue laws.
-
The values of the IRS are:
-
Honesty and integrity: We uphold the public trust in all that we do; we are honest and forthright in all our internal and external dealings.
-
Respect: We treat each colleague, employee and taxpayer with dignity and respect.
-
Continuous improvement: We seek to perform the best that we can today, while embracing change, so that we perform even better in the future.
-
Openness and collaboration: We share information and collaborate recognizing we are a team.
-
Personal accountability: We take responsibility for our actions and decisions and learn and grow from our achievements and mistakes.
-
-
The IRS is led by the Commissioner and Deputy Commissioner who oversee the organization’s operating divisions and integrated support functions. The operating divisions are in turn led by four chief executive positions.
-
Chief Tax Compliance Officer
-
Chief Operating Officer
-
Chief Taxpayer Services
-
Chief Information Officer
-
-
For the functional description of each major IRS organizations, see the applicable IRM section under IRM 1.1, Organization and Staffing.
-
The President of the United States appoints the Commissioner of Internal Revenue, and the Senate confirms the appointee to serve a five-year term.
-
The IRS Commissioner is the head of the IRS and is responsible for ensuring it fulfills its mission of serving taxpayers while administering and enforcing the nation’s tax laws. The Commissioner also represents the agency before Congress and the public.
-
See IRM 1.1.5, Organization and Staffing, Office of the Commissioner for additional information on IRS Commissioner staff, direct reports and functional responsibilities.
-
The IRS Deputy Commissioner reports to the IRS Commissioner and oversees efforts to ensure the IRS fulfills its mission of serving taxpayers and enforcing the nation’s tax laws. The Deputy Commissioner oversees four primary divisions responsible for tax compliance, operations, taxpayer services and information technology.
-
The Chief Tax Compliance Officer (CTCO) reports to the IRS Deputy Commissioner and is responsible for IRS compliance operations. The CTCO oversees the following operations with the heads of each operational organizations as direct reports:
-
Criminal Investigation (CI) - investigates potential criminal violations of the Internal Revenue Code and related financial crimes in a way that fosters America’s confidence in the tax system and compliance with the law. See IRM 1.1.19, Organization and Staffing, Criminal Investigation, for more information.
-
Enterprise Case Management Office (ECMO) - improves business processes and modernizing systems to enhance the taxpayer and employee experience.
-
Large Business and International (LB&I) - handles tax matters for US and foreign businesses with assets over $10 million. LB&I also manages global high-wealth and international individual compliance programs. See IRM 1.1.24, Organization and Staffing, Large Business and International, for more information.
-
Office of Professional Responsibility (OPR) - administers the laws and regulations governing the practice of tax professionals before the Department of the Treasury and the IRS. See IRM 1.1.20, Organization and Staffing, Office of Professional Responsibility, for more information.
-
Return Preparer Office (RPO) - provides comprehensive oversight and support of tax professionals to improve taxpayer compliance. See IRM 1.1.28, Organization and Staffing, Return Preparer Office, for more information.
-
Small Business/Self-Employed (SB/SE) - helps small business/self-employed taxpayers understand and meet their tax obligations, while applying the tax law with integrity and fairness to all. See IRM 1.1.16, Small Business/Self-Employed, for more information.
-
Tax Exempt and Government Entities (TE/GE) - helps employee plans, exempt organizations, and government entities understand and comply with tax laws to protect the public interest. See IRM 1.1.23, Organization and Staffing, Tax Exempt and Government Entities Division, for more information.
-
Whistleblower Office (WO) - administers the IRS Whistleblower program which is designed to receive information that helps uncover tax non-compliance and may pay an appropriate award to the whistleblowers. See IRM 1.1.26, Organization and Staffing, Whistleblower Office, for more information.
-
-
The Chief Operating Officer (COO) reports to the IRS Deputy Commissioner and oversees the IRS's integrated support functions, facilitating economy of scale efficiencies and better business practices. The COO oversees the following operations with the heads of each operational organization as direct reports.
-
Office of the Chief Financial Officer (CFO) - manages a portfolio of corporate-wide activities including strategic planning, performance measurement, budget formulation, budget execution, accounting, financial management and internal controls. See IRM 1.1.21, Organization and Staffing, Chief Financial Office for more information.
-
Office of the Chief Risk Officer (CRO) - oversees the Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) and the Enterprise Audit Management (EAM) programs. The ERM provides a strategic framework to effectively deal with risk across the agency and the EAM provides a collaborative enterprise approach to the IRS TIGTA/GAO audit management process. See IRM 1.1.31, Organization and Staffing, Office of Chief Risk Officer, for more information.
-
Office of the Facilities Management and Security Services (FMSS) - delivers workspace and physical security solutions, safeguards agency assets, and ensures a secure environment for tax administration. See IRM 1.1.17, Organization and Staffing, Facilities Management and Security Services, for more information.
-
Office of the Chief Human Capital Officer (HCO) - provides human capital strategies and tools for recruiting, hiring, developing, retaining, and transitioning a highly skilled and high-performing workforce to support IRS mission accomplishments. See IRM 1.1.22, Organization and Staffing, Human Capital Office, for more information.
-
Office of the Privacy, Governmental Liaison, and Disclosure (PGLD) - protects the sensitive information and privacy of taxpayers and employees. Enhances public trust through authorized disclosure, retention and protection of data and records. See IRM 1.1.27, Organization and Staffing, Privacy, Governmental Liaison and Disclosure, for more information.
-
Office of the Chief Procurement Officer (OCPO) - provides acquisition services for IRS business units and other Treasury bureaus and offices. See IRM 1.1.32, Organization and Staffing, Office of the Chief Procurement Officer, for more information.
-
Office of Research, Applied Analytics and Statistics (RAAS) - leads a data driven culture through innovative and strategic research, analytics, statistics, and technology services to support effective and efficient tax administration in partnership with internal and external stakeholders. See IRM 1.1.18, Organization and Staffing, Research, Applied Analytics and Statistics (RAAS), for more information.
-
-
The Chief, Taxpayer Services reports to the IRS Deputy Commissioner. This role is responsible for all taxpayer services involving all tax return and payment receipt and processing. Additionally, this division oversees pre-refund compliance and filing season activities, taxpayer and preparer outreach, volunteer income tax preparation and grant processing; and taxpayer customer service related activities and taxpayer-facing operations including:
-
Toll-free telephone and face-to-face help
-
Web and chat services
-
Taxpayer Assistance Centers
-
Processing taxpayer correspondence
-
Developing and distributing tax forms and publications, and
-
Issuing notices and letters.
-
-
See IRM 1.1.13, Organization and Staffing, Wage and Investment (renamed Taxpayer Services), for more information.
-
The Chief Information Officer (CIO) reports to the IRS Deputy Commissioner. This role is responsible for delivering information technology services and solutions that drive effective tax administration to ensure public confidence. The Information Technology (IT) organization establishes IRS’s long-term objectives and strategies for improving tax administration through modernizing tax administration systems. See IRM 1.1.12, Organization and Staffing, Information Technology, for more information.
-
The Director of Online Services (OLS) reports to the IRS Deputy Commissioner. This role is responsible for helping IRS business units identify and deliver digital tax services. OLS works closely with IRS business units and Information Technology leadership to deliver strategy, policy and initiatives that create and integrate digital tools and processes into IRS operations. See IRM 1.1.29, Organization and Staffing, Office of Online Services, for more information.
-
Certain key functions report directly to the IRS Commissioner to maintain independence from the other business units. The offices are:
-
Chief Counsel (Counsel) - provides legal interpretation and represents the IRS with complete impartiality, so taxpayers know the law is being applied with integrity and fairness. Counsel reports to the IRS Commissioner on tax matters and reports to the Treasury General Counsel on other matters. See IRM 1.1.6, Organization and Staffing, Chief Counsel, for more information.
-
Chief of Staff (COS) - directs, manages and oversees all policy development, daily operations, and staff activities for the Commissioner. See IRM 1.1.5, Organization and Staffing, Officer of the Commissioner, for more information.
-
Communications and Liaison (C&L) - builds relationships and understanding between the IRS and its stakeholders through effective information sharing to support the IRS mission. See IRM 1.1.11, Organization and Staffing, Communications and Liaison, for more information.
-
Independent Office of Appeals (Appeals) - resolves federal tax controversies with fairness and impartiality for both the taxpayer and government without litigation. Appeals promotes a consistent application and interpretation of, and voluntary compliance with federal tax laws, and enhances public confidence in the integrity and efficiency of the IRS. See IRM 1.1.7, Organization and Staffing, Appeals, for more information.
-
National Taxpayer Advocate (NTA) - helps taxpayers resolve tax problems with the IRS and identifies areas in which taxpayers have problems with the IRS. Taxpayer Advocate Service (TAS) also makes administrative and legislative recommendations to resolve systemic tax issues. See IRM 1.1.8, Organization and Staffing, Taxpayer Advocate Service, for more information.
-
Taxpayer Experience Office (TXO) - develops customer-centric guidelines and expectations to improve the taxpayer experience with all IRS interactions. See IRM 1.1.33, Organization and Staffing, Taxpayer Experience Office, for more information.
-
Direct File - provides eligible taxpayers the option to electronically file their federal tax return for free, directly with the IRS.
-
 )
oswa https:// vle di ou konekte ak sitwèb .gov san danje. Pataje enfòmasyon sansib sèlman sou sit entènèt ofisyèl ki an sekirite.
)
oswa https:// vle di ou konekte ak sitwèb .gov san danje. Pataje enfòmasyon sansib sèlman sou sit entènèt ofisyèl ki an sekirite.