- 9.7.9 Equitable Sharing and Reverse Asset Sharing
- 9.7.9.1 Program Scope and Objectives
- 9.7.9.1.1 Background
- 9.7.9.1.2 Authority
- 9.7.9.1.3 Roles and Responsibilities
- 9.7.9.1.4 Program Management and Review
- 9.7.9.1.5 Program Controls
- 9.7.9.1.6 Acronyms and Terms
- 9.7.9.1.7 Related Resources
- 9.7.9.2 Sharing Authority
- 9.7.9.3 Agencies Eligible to Receive Treasury Equitable Sharing
- 9.7.9.4 How to Participate in the Equitable Sharing Program
- 9.7.9.4.1 Joint Investigation
- 9.7.9.5 How to Apply for an Equitable Share
- 9.7.9.5.1 Federal, State, or Local Agencies
- 9.7.9.5.2 Foreign Countries
- 9.7.9.5.3 Time Limits for Filing an Equitable Sharing Request
- 9.7.9.5.4 Acknowledgments and Advice on Equitable Sharing Requests
- 9.7.9.6 How an Equitable Share is Calculated
- 9.7.9.6.1 Equitable Sharing Involving a Single Item of Tangible Property
- 9.7.9.6.2 Sharing in Joint Operations
- 9.7.9.6.3 Sharing in Task Force and Other Multi-Agency Investigations
- 9.7.9.6.4 Sharing in Adoptive Seizures
- 9.7.9.6.5 The Decision-Makers
- 9.7.9.7 Disposition of Equitable Share
- 9.7.9.8 Uses of Equitably Shared Property
- 9.7.9.9 Accounting for Cash, Proceeds, and Tangible Property
- 9.7.9.10 Reporting Requirements
- 9.7.9.11 Non-Compliance
- 9.7.9.12 Reverse Asset Sharing
- 9.7.9.12.1 Filing and Reporting Requirements
- 9.7.9.12.2 Receipt of Forfeited Property
- 9.7.9.13 Reverse Asset Sharing with State, Local, or Foreign Agencies
- Exhibit 9.7.9-1 Memorandum - Equitable Sharing Request
- Exhibit 9.7.9-2 Memorandum - Treasury Executive Office for Asset Forfeiture High Value Equitable Sharing Request
- Exhibit 9.7.9-3 Federal Contribution Form
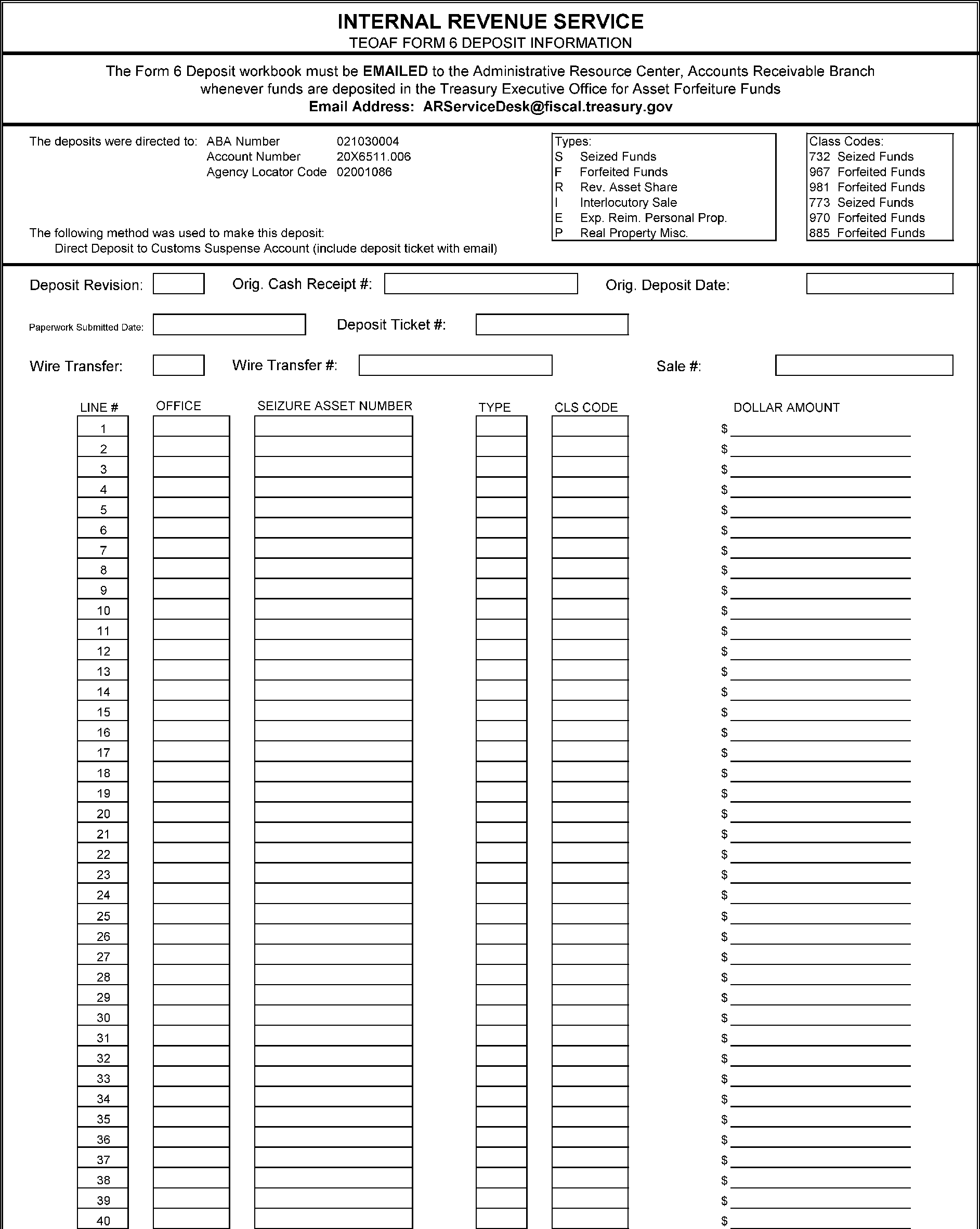
- Exhibit 9.7.9-4 Treasury Executive Office for Asset Forfeiture Form 6, Deposit Information
- 9.7.9.1 Program Scope and Objectives
Part 9. Criminal Investigation
Chapter 7. Asset Seizure and Forfeiture
Section 9. Equitable Sharing and Reverse Asset Sharing
9.7.9 Equitable Sharing and Reverse Asset Sharing
Manual Transmittal
August 29, 2025
Purpose
(1) This transmits revised IRM 9.7.9, Equitable Sharing and Reverse Asset Sharing.
Material Changes
(1) Updated internal controls.
(2) Updated all IRM and website references to quick links throughout the IRM.
(3) Subsection 9.7.9.2(2)(a) removed “taking into account” and added “considering”.
(4) Subsection 9.7.9.3(2) updated to “Equitable sharing does not apply between TFF LEAs, unless the request is for personal property. Monetary instruments cannot be shared between TFF LEAs.”
(5) Subsection 9.7.9.3(4) removed “that results in a” and added “resulting in a”.
(6) Added subsection 9.7.9.3.1(1) “International sharing is governed by 18 USC 981(i), 21 USC 881(e)(1)(E), and 31 USC 9705(h)(2).”
(7) Subsection 9.7.9.3.1(2) updated to current procedures.
(8) Added subsection 9.7.9.3.1(3) “Guidance for international sharing is further discussed in the DOJ Money Laundering and Asset Recovery (MLARS) Asset Forfeiture Policy Manual, Chapter 9 - International Forfeitures, and should be reviewed before any sharing decisions are made.”
(9) Subsection 9.7.9.3.2 updated entire section to current procedures.
(10) Subsection 9.7.9.4 updated to “Joint investigations enable agencies to participate in the equitable sharing program.”
(11) Removed 9.7.9.4.2, Adoption of a Federal, State, Local, or Foreign Seizure.
(12) Subsection 9.7.9.5 updated to current procedures.
(13) Subsection 9.7.9.5.1 updated entire section to current procedures.
(14) Removed subsection 9.7.9.5.2(1)(d) “if applicable, has certification under 22 USC 2291(j)(b) of the foreign country in question.”
(15) Subsection 9.7.9.5.3(1) removed “within 60 days after the date of seizure” and “60-day” and added “no later than 45 days after forfeiture” and “45-day”.
(16) Subsection 9.7.9.5.3(4) updated “60” to “45” days.
(17) Subsection 9.7.9.5.4 updated entire section to current procedures.
(18) Subsection 9.7.9.6(1) added bullet “Treasury mandated expenses (e.g. sequestration fees, etc.).”
(19) Subsection 9.7.9.6(2) updated to “The minimum federal sharing portion will not be less than 20 percent.”
(20) Subsection 9.7.9.6.1(1) removed “state or local agency.”
(21) Removed 9.7.9.6.2, Reimbursement of Federal Costs.
(22) Subsection 9.7.9.7 updated entire section to current procedures.
(23) Removed 9.7.9.9, Weed and Seed Initiative.
(24) Subsection 9.7.9.10 removed “Appendix D of the Guide contains sample bookkeeping procedures that will meet this requirement.”
(25) Subsection 9.7.9.11 updated entire section to current procedures.
(26) Subsection 9.7.9.12(1) removed “Federal Equitable Sharing Agreement and Annual Certification Reports” and added “ESAC”.
(27) Subsection 9.7.9.12(2)(c) updated to “Freeze on receipt or expenditure of shared funds.”
(28) Added subsection 9.7.9.12(d) “Return of shared funds.”
(29) Subsection 9.7.9.13 updated entire section to current procedures.
(30) Subsection 9.7.9.13.1 updated entire section to current procedures.
(31) Subsection 9.7.9.13.2(2) updated to current procedures.
(32) Subsection 9.7.9.14 removed “Federal agencies do” and added “IRS-CI does” removed “have to” and added “must”.
(33) Removed Exhibit 9.7.9-1, Memorandum - Request to Transfer of Property Seized/Forfeited by a Treasury Agency.
(34) Removed Exhibit 9.7.9-2, Memorandum - Request for Transfer of Property Valued at More Than $25,000.
(35) Removed Exhibit 9.7.9-3, Form TD F 92-22.46 and Supplemental Instructions, Request for Transfer for Property Seized/Forfeited by a Treasury Agency.
(36) Removed Exhibit 9.7.9-4, Form TD F 90-22.51, Equitable Sharing Form.
(37) Removed Exhibit 9.7.9-5, Form #6, Deposit Information.
(38) Added Exhibit 9.7.9-1, Memorandum - Equitable Sharing Request.
(39) Added Exhibit 9.7.9-2, Memorandum - Treasury Executive Office for Asset Forfeiture High Value Equitable Sharing Request.
(40) Added Exhibit 9.7.9-3, Federal Contribution Form.
(41) Added Exhibit 9.7.9-4, Treasury Executive Office for Asset Forfeiture Form 6, Deposit Information.
(42) Editorial changes made throughout the IRM that did not result in substantive changes but contributed to clarity of the subject matter.
Effect on Other Documents
This IRM supersedes IRM 9.7.9 dated February 24, 2025.Audience
Criminal InvestigationEffective Date
(08-29-2025)
Justin H. Campbell
Acting Deputy Chief, Criminal Investigation
for
Guy A. Ficco
Chief, Criminal Investigation
-
Purpose: This section provides detailed guidelines for the roles and responsibilities of Criminal Investigation employees and government partners, as it relates to equitable sharing and reverse asset sharing.
-
Audience: All Criminal Investigation employees.
-
Policy Owner: Executive Director, Global Operations Policy & Support.
-
Program Owner: Director, Asset Recovery and Investigative Services within Global Operations Policy & Support.
-
Primary Stakeholders: All Criminal Investigation employees.
-
Contact Information: To make changes to this IRM email *CI-HQ-IRM.
-
One of the goals of the Department of the Treasury Asset Forfeiture Program is to encourage joint operations among federal, state, and local law enforcement agencies, as well as foreign countries. The equitable sharing program has proved invaluable in fostering enhanced cooperation among federal, state, local, and foreign law enforcement agencies.
-
The Department of the Treasury and Department of Justice "Guide to Equitable Sharing for State, Local, and Tribal Law Enforcement Agencies" , aka the “Guide”, contains policies and procedures applicable to the sharing of assets that are seized and forfeited by law enforcement agencies participating in the Treasury Forfeiture Fund. The Guide was designed not only for the Treasury Forfeiture Fund agencies, but for any federal, state, or local law enforcement agency that files an equitable sharing request with a Treasury Forfeiture Fund law enforcement agency.
-
IRM 9.7.9 closely follows the format of and contains excerpts from the Guide. The Guide can be found on the U.S. Department of Treasury website.
-
This section will also cover reverse asset sharing requests.
-
See 28 USC 524(c), Availability of Appropriations, for the delegated authority relating to IRM 9.7.9, Equitable Sharing and Reverse Asset Sharing.
-
Federal law establishes the authority of the Secretary of the Treasury to share federally forfeited property with participating federal, state, and local law enforcement agencies.
-
The Director, Asset Recovery and Investigative Services is responsible for developing, maintaining, and overseeing this IRM and ensuring compliance with current policies and procedures.
-
The Director, Asset Recovery and Investigative Services will:
-
Review this IRM annually for procedural, operational, and editorial changes.
-
Ensure internal control content is complete, accurate, and reviewed annually.
-
Update this IRM when content is no longer accurate.
-
Incorporate interim guidance into the next revision of this IRM section prior to the expiration date.
-
-
The Director, Asset Recovery and Investigative Services will review this IRM to ensure compliance with applicable laws and regulations and assure their program objectives and procedures are efficiently and effectively accomplished.
-
The following table lists the acronyms and terms used throughout this IRM section and their definitions:
Acronym Definition AFC Asset Forfeiture Coordinator AFTRAK Asset Forfeiture Tracking and Retrieval System ARIS Asset Recovery and Investigative Services AUSA Assistant United States Attorney CATS Consolidated Asset Tracking System CI Criminal Investigation CSD Center for Science and Design DOJ Department of Justice EQSH Equitable Sharing EQSH Guide Department of the Treasury and Department of Justice Guide to Equitable Sharing for Foreign Countries and Federal, State, and Local Law Enforcement Agencies ESAC Equitable Sharing Agreement and Certification FCF Federal Contribution Form FNS USDA Food and Nutritional Services IPAC Intra-Governmental Payment and Collection System LEA Local Law Enforcement Agencies MLARS Money Laundering and Asset Recovery Section MPA Management and Program Analyst OIG/USDA Office of Inspector General, U.S. Department of Agriculture OMB Office of Management and Budget RASR Reverse Asset Sharing Requests SAC Special Agent in Charge SSA Supervisory Special Agent TEOAF Treasury Executive Office for Asset Forfeiture TFF Treasury Forfeiture Fund USAO United States Attorney’s Office USPIS United States Postal Inspection Service
-
18 USC 666, Crimes and Criminal Procedure, Theft or bribery concerning programs receiving federal funds.
-
18 USC 981(i), Crimes and Criminal Procedure, Civil forfeiture.
-
18 USC 1001, Fraud and False Statements, Crimes, Statements or entries generally.
-
21 USC 881(e)(1)(E), Control and Enforcement, Forfeitures.
-
28 USC 524(c), Department of Justice, Availability of appropriations, Department of Justice Assets Forfeiture Fund.
-
31 USC 9705(h)(2), Money and Finance, Department of the Treasury Forfeiture Fund.
-
Guide to Equitable Sharing for State, Local, and Tribal Law Enforcement Agencies.
-
IRM 9.7.5, Forms, Processing, and Documentation.
-
Federal law establishes the authority of the Secretary of the Treasury to share federally forfeited property with participating federal, state, and local law enforcement agencies (LEA).
-
The intent of Congress in the sharing of forfeited property, as stated, is to ensure that any property shared with a law enforcement agency:
-
Has a value that bears a reasonable relationship to the degree of direct participation to the law enforcement effort resulting in the forfeiture, considering the total value of all property forfeited and the total law enforcement effort with respect to the violation of law on which forfeiture is based; and,
-
Will serve to encourage further cooperation between the recipient agency and federal law enforcement agencies.
-
-
Any federal, state, or local LEA, or foreign country, that directly participates in an investigation or prosecution that results in a federal forfeiture by a Treasury Forfeiture Fund (TFF) LEA may request an equitable share of the net proceeds of the forfeiture.
-
Equitable sharing does not apply between TFF LEAs, unless the request is for personal property. Monetary instruments cannot be shared among TFF LEAs.
-
United States Attorney's Offices (USAO) are not eligible to receive Treasury equitable sharing.
-
State and local prosecutor offices that directly participate in an investigation or prosecution resulting in a Treasury federal forfeiture are eligible to receive Treasury equitable sharing. Refer to the Guide to Equitable Sharing for State, Local, and Tribal Law Enforcement Agencies, known as the "EQSH Guide" , for examples of ways in which state and local prosecutors may qualify for an equitable share.
-
Requesting federal agencies must be participants in an authorized forfeiture fund that has statutory authority to deposit and spend forfeiture proceeds.
-
International sharing is governed by 18 USC 981(i), 21 USC 881(e)(1)(E), and 31 USC 9705(h)(2).
-
The Attorney General and Secretary of the Treasury have sole discretion to determine sharing of any forfeited currency, sale proceeds, or property with the foreign country that participated in the seizure or forfeiture, if such transfer:
-
Has been agreed to by the Department of Justice (DOJ).
-
Has been approved by the Secretary of State.
-
Is authorized in an international agreement between the United States and the foreign country.
-
-
Guidance for international sharing is further discussed in DOJ Money Laundering and Asset Recovery (MLARS) Asset Forfeiture Policy Manual and should be reviewed before any sharing decisions are made.
-
The Office of Inspector General, US Department of Agriculture (OIG/USDA), the DOJ, the U.S. Postal Inspection Service (USPIS), and the Department of the Treasury entered into a Memorandum of Understanding to establish the participation of OIG/USDA in the DOJ Asset Forfeiture Program and DOJ Asset Forfeiture Fund for forfeitures after May 5, 1998. As a participant in the DOJ Asset Forfeiture Fund, OIG/USDA is eligible to file for equitable shares that correspond to their degree of participation in law enforcement investigative efforts resulting in forfeitures by TFF LEAs. OIG/USDA is also permitted, by statute, to file petitions for remission for 100 percent of the proceeds of the forfeited assets as a victim.
-
Pursuant to CI internal policy issued October 2013, in all cases where USDA Food and Nutritional Services (FNS) is the victim or has an ownership interest in the proceeds of forfeited assets, the USDA FNS will file a petition for remission.
-
The Director, ARIS, may transfer for official use, personal property valued at $25,000 or less to an agency that did not participate in the seizure or forfeiture upon request by memorandum from the Special Agent in Charge (SAC). See Exhibit 9.7.9–1. A request for transfer of property valued at more than $25,000 will be submitted by memorandum from the SAC to the Director, Treasury Executive Office for Asset Forfeiture (TEOAF), through ARIS. See Exhibit 9.7.9–2.
-
If the requesting agency is not a Treasury LEA, it shall pay costs incurred by the TFF in connection with the forfeiture and transfer of any property.
-
Joint investigations enable agencies to participate in the equitable sharing program.
-
Requests for equitable shares must be submitted using Form TD F 92-22.46, Request for Transfer of Property Seized/Forfeited by a Treasury Forfeiture Fund Participating Agency, within forty-five (45) days following the forfeiture date of the asset(s) being requested.
-
Federal agencies must utilize a Federal Contribution form (FCF) to request equitable sharing for seizures in a joint investigation. See Exhibit 9.7.9-3.
-
After the seizure in a joint investigation, a federal, state, or local agency may request a share of the property by submitting Form TD F 92-22.46 to IRS-CI.
-
A separate FCF or Form TD F 92-22.46 must be completed for each seizure. When multiple assets are seized, one FCF or Form TD F 92-22.46 may be filed with an attached listing of all the assets seized, if sharing percentages are equal for each asset. If sharing percentages are different, a separate FCF or Form TD F 92-22.46 must be filed.
-
The Secretary of the Treasury, pursuant to statutory authority, may share forfeited currency or proceeds with countries that participated directly or indirectly in any acts that led to the seizure or forfeiture, if the sharing:
-
Has the concurrence of the DOJ,
-
Has the approval of the Department of State,
-
Is authorized in an international agreement between the United States and the foreign country.
-
-
The Director, TEOAF makes the ultimate decision whether and how much to share after review and approval by the Department of State. No United States representative has the statutory authority to commit to asset sharing in any given case until an international forfeiture sharing agreement has been approved at the delegated levels of the Department of the Treasury (or Justice) and State.
-
A foreign country may request a share of the property by contacting the US Embassy or country attaché via a letter of request. The embassy should forward the letter of request to the appropriate field office.
-
Equitable sharing requests should be submitted no later than 45 days after forfeiture. The 45–day rule may be waived by the Director, ARIS, upon a written request stating the reasons that justify a waiver for the late submission of the equitable sharing request. The request for a waiver must accompany the Form TD F 92-22.46.
-
The date of seizure is generally the date the property is physically seized and taken into custody by CI. This is also true for criminal forfeitures where property is not seized until the court enters a preliminary order of forfeiture. In the case of a civil judicial forfeiture involving real property or other property not seized until a final judgment or order of forfeiture is entered, the date of seizure is the "post and walk" date or the date the warrants of arrest in rem are executed.
-
For property that is seized as evidence, the date of seizure for forfeiture is generally the evidence seizure date or the initial date when action is taken to commence forfeiture proceedings against the property.
-
In civil or criminal judicial forfeitures, an agency may amend its Form TD F 92-22.46 within 45 days after forfeiture to reflect any continued participation in the case.
-
No equitable sharing request will be considered after two years from the date the forfeited property is disbursed, deposited into the TFF, or otherwise disposed of.
-
IRS-CI should keep partner agencies apprised of the status of their equitable sharing request at key points in the equitable sharing process.
-
Upon the Receipt of an Equitable Sharing Request - Within 30 days of the receipt of an equitable sharing request, IRS-CI shall provide the submitting state or local agency with a written notice of receipt and point-of-contact information for future updates.
-
Upon Issuance of Payment - Within 30 days of receiving TEOAF notification that a payment has been made, IRS-CI shall provide the recipient state or local agency with written notice that includes the payment amount, the asset identification number related to the payment, and the payment transmittal date.
-
-
Forfeiture, like all legal proceedings, takes time. Equitable sharing may occur only after the federal forfeiture has been completed, the United States has taken clear title to the property, and a final sharing decision has been made by the appropriate official. Common causes of delay are listed in the EQSH Guide.
-
Equitable sharing is based on the net proceeds of the forfeiture. Net proceeds are calculated as follows: Gross receipts from forfeiture or the sale of the forfeited property, less:
-
Qualified third-party interests.
-
IRS-CI investigation-related expenses.
-
Restitution/remission to victims through the petition process.
-
Any award paid to a federal informant regarding the asset.
-
Treasury property management expenses.
-
Treasury mandated expenses (e.g. sequestration fees, etc.)
-
Any reimbursements from the TFF to the requesting agency that relate to the particular seizure.
-
Equals net proceeds available for equitable sharing.
-
-
The minimum federal sharing portion will not be less than 20 percent.
-
In cases where only a single item of tangible property (e.g., a vehicle) is forfeited and a federal agency or foreign country requests that item rather than proceeds from the sale of the property, the TFF must recover its costs and its equitable share. If the requesting agency is unable to pay the costs and equitable share, the property shall be sold, and the proceeds equitably distributed according to the formula in the previous paragraph. Exceptions to this requirement will be conservatively granted by ARIS upon written assurances that:
-
The requesting agency lacks funds or authority to make such payments.
-
The forfeited item will fill a demonstrated need of the requesting agency.
-
-
Federal law mandates that sharing in joint investigations reflects the degree of direct participation of the requesting agency in the law enforcement effort resulting in the forfeiture. Normally, this is determined by comparing the number of investigative hours expended by the requesting agencies. The hours worked include all hours worked by investigators or professional analysts and technicians through the completion of the forfeiture directly attributed to the forfeiture action. Support staff time may not be used in an agency's determination of investigative hours. The final determination of sharing percentages will not be done until after the property has been forfeited and all of the participating agency's total contributions to the seizure/forfeiture have been determined.
-
The following additional factors will be considered where the hours devoted do not adequately reflect the degree of participation of the requesting agency:
-
Did the agency originate all of the information leading to the seizure?
-
Did an agency provide unique and indispensable assistance?
-
Could the state or local agency have achieved forfeiture under state law, but joined forces with the United States/CI to conduct a more effective investigation?
-
-
For examples of situations that may apply to the questions listed above, refer to the EQSH Guide.
-
Many task forces involving federal, state, and local law enforcement have pre-agreed equitable sharing arrangements based upon relative numbers of personnel and other contributions to the task force operation. These pre-agreed percentages will be honored when:
-
The agreement is generally consistent with the Department of the Treasury equitable sharing policy.
-
The agreement is in writing.
-
The decision-maker is satisfied that the percentages agreed upon continue to reflect the true overall agency contributions to the task force.
-
The task force has a well-defined subject area or organization target as its focus and, the specific seizures are part of the overall investigative function of the task force.
-
-
Refer to the EQSH Guide for more information regarding a formal chartered task force, multi-agency cases, and task force agreements.
-
The authority to approve equitable sharing of assets forfeited in a single forfeiture proceeding where the appraised value of the assets is less than $1,000,000 has been delegated to the Director, ARIS. Exceptions are those involving foreign sharing windfall situations or the transfer of real property, which requires approval from the Director, TEOAF.
-
Where the forfeited assets are valued at $1,000,000 or more, and in all cases involving the transfer of real property, the Director, TEOAF, must approve the amount of the equitable share.
-
The Assistant United States Attorney (AUSA) will be offered the opportunity for input before final sharing decisions are made when the forfeiture is a civil judicial or criminal forfeiture.
-
All forfeiture cases involving foreign equitable sharing requests must be approved by the Director, TEOAF, and the Department of State.
-
The TEOAF will notify the field office when equitable sharing payments are sent to the requesting agency(ies) electronically.
-
If the SAC wants to make a formal presentation to thank the partner agencies for their participation and to encourage future joint efforts, the field office will be responsible for the logistics. The AFC should consult ARIS to confirm the status of the equitable sharing payment(s).
-
Formal presentation logistics may involve coordination with the IRS-CI Center for Science and Design (CSD) Trial Illustration Unit.
-
The EQSH Guide provides detailed guidance to requesting agency's permissible and impermissible uses of equitable shared property.
-
All participating state and local law enforcement agencies must implement standard accounting procedures and internal controls to track equitably shared monies and tangible property in accordance with the general accounting procedures and compliance requirements contained in the EQSH Guide.
-
Federal Equitable Sharing Agreement and Certification -- As a prerequisite to participating in the Department of the Treasury Equitable Sharing Program, a state or local LEA must submit a signed Equitable Sharing Agreement and Certification (ESAC) and affidavit to MLARS on eShare. Federal agencies are exempt from this requirement.
-
Compliance -- State and local LEAs must annually submit an ESAC signed by both the head of the LEA and the head of the governing body with budgetary authority over the LEA within two months following the close of the agency’s fiscal year.
-
Annual Audit -- Audits will be conducted as provided by the Single Audit Act Amendments of 1996 and Office of Management and Budget (OMB) Uniform Administrative Requirements, Cost Principles, and Audit Requirements for Federal Awards.
-
Non-compliance with the policies of the EQSH Guide including the failure to timely submit the ESAC, may subject recipient agencies to sanctions.
-
The sanctions include one or more of the following:
-
Denial of an agency's sharing request,
-
Temporary or permanent disbarment from further participation in the sharing program,
-
Freeze on receipt or expenditure of shared funds,
-
Return of shared funds,
-
Civil enforcement actions in US District Court for breach of contract,
-
Federal criminal prosecution for false statements under 18 USC 1001 or fraud involving theft of federal program funds under 18 USC 666, or other sections of the criminal code, as applicable.
-
-
IRS-CI routinely participates in joint investigations where a DOJ LEA is the lead seizing agency. The lead seizing agency processes the seizure through forfeiture to disposition.
-
To receive an equitable share of the forfeited property resulting from IRS-CIs participation in an investigation, a sharing request must be submitted via an electronic FCF on the eShare portal. To submit requests on eShare, IRS-CI must be added as s sharing agency in the DOJ’s Consolidated Asset Tracking System (CATS) by the seizing DOJ LEA.
-
DOJ maintains an Asset Forfeiture Fund, similar to TFF, where all forfeited cash and proceeds from sales of forfeited property are deposited. The DOJ Asset Forfeiture Fund serves the same purpose and is subject to similar restrictions as the TFF. The DOJ Asset Forfeiture Fund policy allows a maximum asset sharing amount of 80 percent. DOJ’s policy restricts equitable sharing on plea agreement payments unless the Treasury agency provided direct assistance in obtaining the payment(s).
-
It is the responsibility of IRS-CI to file a request for an equitable share of forfeited property when IRS-CI participated in investigations with DOJ LEA.
-
Reverse asset sharing requests must be submitted to the DOJ seizing agency within 45 calendar days of the forfeiture on eShare. The 45-day rule can only be waived upon a request. The waiver request must be submitted via the electronic FCF to the DOJ seizing agency, stating the reasons for the late submission of the request and/or providing justification for the waiver. Failure to adhere to these rules may result in delayed or lost shares to the TFF.
-
The SAC must approve seizure investigative activities in CIMIS for any investigation where IRS-CI participates in the seizure and forfeiture with a DOJ LEA. A pdf copy of the FCF, containing the information must be signed by the SAC and maintained in the field office’s files. All RASR’s must be submitted in eShare and simultaneously recorded in the Asset Forfeiture Tracking and Retrieval System (AFTRAK). See IRM 9.7.5, Forms, Processing, and Documentation.
-
The AFC should use AFTRAK to monitor open reverse asset sharing requests. It is the responsibility of the AFC to obtain status updates by contacting the seizing agency. Status updates can also be found by checking on eShare.
-
If IRS-CI is denied the ability to apply for equitable sharing by a DOJ LEA or fails to receive an equitable share in return for their participation, the responsible Supervisory Special Agent (SSA) or SAC is encouraged to attempt resolution at the field office level. If resolution cannot be achieved, the issue should be forwarded to ARIS for resolution at the TEOAF and/or DOJ level.
-
Tangible property received from a federal agency through reverse asset sharing may be placed into official use in accordance with IRS-CI guidelines. Forfeited cash and proceeds from the sale of forfeited property must be deposited to the TFF.
-
RASR payments are disbursed using the Intra-Governmental Payment and Collection System (IPAC). For payments disbursed via a check, the check must be immediately sent to ARIS with a completed TEOAF Form #6, found on the ARIS SharePoint site. See Exhibit 9.7.9-4, TEOAF Form #6, Deposit Information.
-
IRS-CI does not have the authority to directly accept equitable shares of property or tangible items from state, local, or foreign law enforcement agencies. Such shares must be treated as gifts to the federal government and permission to accept the gift must be sought from Treasury's Assistant Secretary for Management before accepting any such property.



Please click here for the text description of the image.

Please click here for the text description of the image.

Please click here for the text description of the image.

Please click here for the text description of the image.

 )
또는 https:// 는 안전하게 .gov 웹사이트에 접속했다는 뜻입니다. 오직 공식, 보안 웹사이트 상에서만 민감한 정보를 공유하십시오.
)
또는 https:// 는 안전하게 .gov 웹사이트에 접속했다는 뜻입니다. 오직 공식, 보안 웹사이트 상에서만 민감한 정보를 공유하십시오.